Turkey Tail is a common type of mushroom, scientifically known as Trametes versicolor, that is believed to have significant health benefits, particularly for gut health. Its impact on gut health stems from its rich polysaccharide content, including a type known as polysaccharopeptides (PSPs). These have been shown to modulate the gut microbiota, fostering a diverse and balanced environment that can enhance digestive functions and boost immunity.
Delving deeper into this intriguing subject, our subsequent exploration will take us on a journey to understand the critical components of Turkey Tail mushroom and the science behind its health benefits. We'll also provide practical tips for adding this unique mushroom to your diet and answer frequently asked questions about its role in promoting gut health. This journey is not just about introducing a new health supplement; it's about exploring the potential of nature to heal, nurture, and strengthen our bodies from the inside out.
The Intricacies of Gut Health and the Role of the Immune System

The Importance of Gut Health: More Than Just Digestion
Our gut health goes beyond just aiding in digestion. Our gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, including gut bacteria, which play a critical role in our overall health.
Having healthy gut bacteria helps our body function optimally. Changes in these beneficial bacteria could lead to common problems related to gut health, such as irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel diseases, obesity, and more.
The Role of Gut Microbiota in Overall Health and Immunity
The gut microbiota, or gut microbiome, can significantly influence our immune system health. This intricate community of microorganisms educates our immune cells and helps orchestrate the immune response to pathogens. A balanced gut microbiome supports digestive tract health and boosts our immune health.
Research shows that(1) our gut microbiota can even influence the functioning of distant organs. For instance, certain gut bacteria can support liver health, and a balanced microbiome can also improve the immune system's ability to fight breast cancer. Traditional Chinese medicine has recognized the concept of a balanced gut for centuries, validating our recent scientific discoveries.
The Problem with Imbalance: Disruptions to Gut and Immune Health
When the balance of our gut microbiome is disrupted, we encounter common problems related to gut health. An imbalanced gut, often lacking in healthy bacteria, can affect the health of the gastrointestinal tract and compromise the immune system, making us more susceptible to diseases.
Functional mushrooms like Turkey Tail, highly revered in traditional Chinese medicine, can help restore this balance. The bioactive ingredients in mushrooms improve gut health in multiple ways. For example, Turkey Tail contains beneficial compounds such as protein-bound polysaccharides and polysaccharide peptides, which can encourage the growth of beneficial bacteria and support the immune system.
The benefits of medicinal mushrooms like Turkey Tail have also shown the potential to enhance the immune system's response against breast cancer by stimulating natural killer and white blood cells. Furthermore, these edible mushrooms, classified as plant foods, have been used to improve therapeutic efficiency in treating various illnesses.
The Power of Turkey Tail Mushroom: An Ancient Solution for Modern Health Concerns
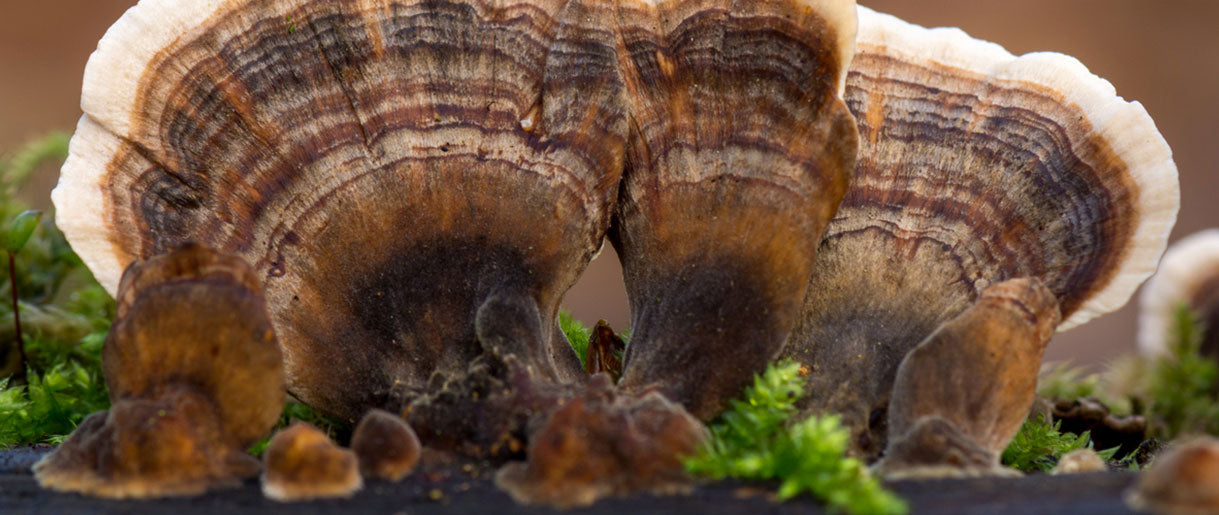

The Colorful History of Turkey Tail Mushroom
One of the most recognizable types of medicinal mushrooms, the Turkey Tail Mushroom, is named for its striking resemblance to a turkey's colorful, fan-like tail. Known as Yun Zhi in China and Kawaratake in Japan, which translates to "cloud mushroom," this fascinating fungus has a long history in traditional medicine across Asia.
Trametes versicolor were used in traditional medicine to treat various ailments and promote longevity. The benefits of Turkey Tail have been studied for years, showing clear and consistent changes in health outcomes, particularly for immune system function and cancer treatment.
The Nutritional Powerhouse: What Turkey Tail Mushrooms Contain
Turkey Tail mushrooms are a treasure trove of nutrients and beneficial compounds. They are known to bolster the immune system and foster healthy bacteria in the gut. Research shows that Trametes versicolor contains polysaccharopeptides that can stimulate the immune response and support the creation of cancer-fighting cells.
This immune support is critical to Turkey Tail mushroom benefits, contributing to its widespread use in improving therapeutic efficiency. Regular consumption of Trametes versicolor can lead to beneficial changes in the immune system, supporting overall health.
Turkey Tail in Traditional Medicine and Modern Therapies
The benefits of Turkey Tail mushrooms have been harnessed in traditional medicine to treat various health conditions. Recent studies reveal the Turkey Tail cancer treatment benefits, improving therapeutic efficiency in treating various types of cancer, including colorectal, gastrointestinal, and gastric cancer.
Trametes versicolor is believed to enhance the immune response, stimulating the production of white blood cells and amplifying the therapeutic efficacy of cancer treatment. In recent years, Turkey Tail mushroom benefits have been tapped to supplement conventional therapies, offering an integrative approach to health.
The Science Behind Turkey Tail Mushroom: Unveiling Its Gut Health Benefits
Key Studies Uncover the Wonders of Turkey Tail Mushroom
Scientific research has significantly expanded our understanding of Turkey Tail mushroom benefits, especially regarding gut health. Numerous studies conducted over the years have explored how Turkey Tail mushrooms interact with our gut, leading to findings that support traditional medicinal claims.
One pivotal study(2) explored how the active compounds in Trametes versicolor, including polysaccharide peptide PSP and phenolic compounds, could enhance gut health. The study found that these compounds could increase the population of certain good bacteria in the gut, improving overall gut health.
Another noteworthy study(3) focused on how Turkey Tail mushrooms could improve therapeutic efficacy in managing insulin resistance, a condition often linked to gut health. The findings revealed promising potential, validating the medicinal claims of Turkey Tail mushrooms.
The Key Findings: How Turkey Tail Mushroom Boosts Gut Health
Several studies have shown that Turkey Tail mushrooms can positively impact gut health. The polysaccharide peptide PSP found in Trametes versicolor stimulates dendritic cells, critical immune system components, which can result in improved gut health.
A particular focus has been on how Turkey Tail mushrooms can promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria. Research shows that regular consumption of Turkey Tail mushrooms may increase beneficial bacteria in the gut, which plays a vital role in maintaining gut health and boosting the immune system. These findings offer scientific backing for using Trametes versicolor in promoting gut health.
The Triad of Benefits: How Turkey Tail Mushroom Promotes Gut Health
Boosting Immunity: The First Line of Defense
One of the most remarkable turkey tail mushroom benefits is its potential to boost the immune system. The active compounds in turkey's tail have shown promise in enhancing immune responses, which can indirectly contribute to better gut health.A robust immune system can more effectively guard against pathogens that might compromise gut health.
Research indicates that(4) Turkey Tail mushroom may stimulate the production of immune cells, enhancing our body's ability to fight off infections. Moreover, these mushrooms can act as a prebiotic, nourishing certain bacteria that play a critical role in immunity.
Enhancing Digestive Functions: Aiding the Body's Natural Processes
Turkey tail mushroom benefits extend to enhancing digestive functions as well. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, turkey tail may help facilitate digestion, reduce inflammation, and prevent digestive disorders.
Compounds found in turkey's tail, such as polysaccharides and triterpenes, contribute to its digestive benefits. These compounds can stimulate the secretion of digestive enzymes, enhancing the body's ability to break down and absorb nutrients from food.
Modulating Gut Microbiota: Balancing the Ecosystem Within
Turkey tail mushroom benefits are perhaps most directly seen in their impact on gut microbiota. These mushrooms are rich in polysaccharides, compounds that certain bacteria in our gut can feed on. By providing this nourishment, turkey tail may help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
A balanced gut microbiota is essential for overall health, affecting everything from digestion to mood. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting harmful ones, turkey tail mushrooms contribute to a healthy, balanced gut ecosystem.
Embracing Turkey Tail Mushroom: How to Incorporate It into Your Diet

The Savvy Shopper: A Guide to Buying Turkey Tail Mushroom Products
When purchasing Turkey Tail products, there are several factors to consider. First and foremost, always look for a reputable source. Companies that specialize in medicinal mushrooms are often the best bet. When shopping, look for Turkey Tail extract or Turkey Tail powder made from organically grown, non-GMO mushrooms to ensure you get a product free from pesticides and harmful additives.
Product labels are an essential source of information. High-quality Turkey Tail extracts typically list the concentration of active ingredients, such as polysaccharides. The higher the concentration, the more potent the product is likely to be. Also, consider the best format that suits your needs—Turkey Tail extract, powder, or dried Turkey Tail mushrooms.
Choosing Your Form: Powder, Capsules, Tea, and More
Turkey Tail mushrooms are versatile and can be consumed in several forms. Turkey Tail extracts and capsules are excellent choices for those who prefer convenience. They are easy to take, and the Turkey Tail mushroom dosage is straightforward to control.
Turkey Tail powder offers more flexibility—the mushroom powder can be mixed into smoothies, soups, or other dishes. Dried Turkey Tail mushrooms can make a soothing tea for a warming drink. Turkey tail mushroom tea is a traditional method of consumption that brings out the mushroom's beneficial compounds.
Cooking with Turkey Tail: Easy and Delicious Recipes
Incorporating Turkey Tail mushroom extract or powder into your diet can be as simple as adding it to everyday meals. Here are a couple of easy recipes:
Turkey Tail Mushroom Smoothie
Start your day with a nutrient-rich smoothie. Blend a handful of your favorite fruits with a cup of almond milk, a scoop of protein powder, and a teaspoon of Turkey Tail extract or powder.
Turkey Tail Mushroom Soup
Try adding Turkey Tail powder to your favorite soup for a comforting meal. Mix in a couple of teaspoons of the powder or a handful of dried Turkey Tail mushrooms into the soup while cooking.
Remember, consistency is vital to experience the benefits of Turkey Tail mushrooms. Try to incorporate them into your diet regularly and combine this with a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle for the best results.
Cautionary Tales: Precautions and Side Effects of Turkey Tail Mushroom

The Flip Side: Possible Side Effects of Consuming Turkey Tail Mushroom
While the benefits of Turkey Tail mushroom for gut health are abundant, it's also crucial to be aware of the potential side effects of mushroom supplements. Most people can consume Turkey Tail mushrooms without any adverse reactions, but like all foods and supplements, they may not agree with everyone.
Common side effects, although rare, can include digestive discomfort such as gas, bloating, or darkened stools. Some individuals might also experience changes in bowel movements. Most of these side effects are mild and usually disappear once your body adjusts to the new supplement.
It's also worth noting that Turkey Tail mushrooms could interact with certain medications, including those for managing diabetes or autoimmune conditions, due to their impact on the immune system. It's always recommended to talk to your healthcare provider if you're on any medication before starting a new supplement regimen.
FAQs About Turkey Tail Gut Health
Can Children And Teenagers Take Turkey Tail Mushrooms For Gut Health?
Turkey Tail mushrooms have been generally recognized as safe and are widely used in various forms around the world. However, most research on the effects and safety of Turkey Tail mushrooms has been conducted on adults. Therefore, it is unclear whether they are safe or beneficial for children or teenagers.
Children and teenagers have different nutritional needs and physiological characteristics than adults. Therefore, they might react differently to supplements. Always consult a pediatrician or a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, including Turkey Tail mushrooms, in children or teenagers.
Are There Any Vegan Or Vegetarian-Friendly Turkey Tail Supplements Available?
Yes, many Turkey Tail mushroom supplements are available on the market that are vegan and vegetarian-friendly. These are usually made from the mushroom's fruiting body and do not contain any animal products.
However, not all supplements are created equal. Some capsule forms of supplements might use gelatin, which is an animal-derived product. Therefore, if you're following a vegan or vegetarian diet, it's essential to read the product label carefully. Look for supplements stating they are "vegan" or "vegetarian."
How Long Does It Take To See The Effects Of Turkey Tail On Gut Health?
The time it takes to see the effects of Turkey Tail mushrooms on gut health can vary greatly depending on individual factors such as diet, lifestyle, and overall health status. For some people, positive changes may be noticed within a few weeks of consistent use, while for others, it might take a few months.
Turkey Tail mushroom promotes a healthy balance of gut bacteria, supporting immune function and aiding in digestion, and these effects take place over time. It's not a quick fix but a natural supplement for regular, long-term use.
Is It Safe To Take Turkey Tail Mushrooms Along With Probiotics?
Taking Turkey Tail mushrooms and probiotics, in general, should be safe for most people. Turkey Tail mushrooms contain compounds that can support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which aligns well with the purpose of probiotic supplements—to increase the diversity and abundance of beneficial bacteria in your gut.
However, everyone's body responds differently, and some people might experience digestive discomfort when taking multiple supplements at once. If you decide to start taking both, it's a good idea to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it to allow your body time to adjust.
Can I Take Turkey Tail Mushrooms While Pregnant Or Breastfeeding?
The safety of taking Turkey Tail mushrooms during pregnancy or breastfeeding is poorly studied. While Turkey Tail mushrooms have been used for centuries in traditional medicine and are generally considered safe, it's unclear whether they are any specific risks or benefits to using them during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding are periods of significant physiological changes, and it's crucial to be cautious about dietary supplements during these times. Some mushroom supplements can affect hormone levels or have other effects that could impact the baby's health. Before starting any new supplement during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, it's recommended to consult with a healthcare provider.
Key Takeaways
Turkey Tail mushroom has proven a potent ally for our overall wellness, from its unique role in bolstering our immune systems to its vital support to our gut health. By fostering healthy gut bacteria, enhancing digestive functions, and modulating the gut microbiota, this remarkable fungus offers significant benefits for our internal ecosystem.
But the story of Turkey Tail mushroom and its intersection with our health does not end here. As research unfolds, we might find even more intriguing facets of this remarkable mushroom. We encourage you to stay curious, continue to educate yourself, and engage in conversations about the intriguing world of medicinal mushrooms. After all, the more we learn, the better we can harness these natural resources for our health.
We're interested in hearing from you! Have you used Turkey Tail mushrooms before? After learning about their gut health benefits, are you considering incorporating them into your wellness routine? Or maybe you have a personal story or insight you'd like to share? Whatever it is, feel free to leave a comment below.
Your thoughts and experiences enrich our community, fostering a dynamic exchange of ideas and insights. We're all here to learn from each other, and we look forward to hearing your unique perspective.
References
- Role of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Breast Cancer and Novel Approaches in Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment, (1)https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8405251/
- Effects of polysaccharopeptide from Trametes versicolor and amoxicillin on the gut microbiome of healthy volunteers: a randomized clinical trial, (2)https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25006989/
- A Critical Review on Health Promoting Benefits of Edible Mushrooms through Gut Microbiota, (3)https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5618583/
- The mycelium of the Trametes versicolor (Turkey tail) mushroom and its fermented substrate each show potent and complementary immune activating properties in vitro, (4)https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6889544/









Let Us Know Your Comments